Chapter 101.5 – Using Conservation of Energy to Determine the Energy Balance of a SPA System
Conservation of Energy
Similar to the approach described for the conservation of mass, the principle of conservation of energy can also be applied to the SPA system. The energy budget (also called energy balance) we described in the previous section and in Fig. 1-3 can be determined for the surface of the unit area (Fig. 1-5).
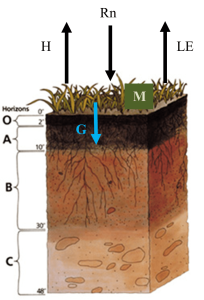
The energy balance of a vegetated surface (Fig. 1.5) is given by:
Equation 2
Click on each “i” symbol to see the definition of each component of Equation 2:
The LE is described as latent heat (not visible or detected) because it does not cause a change in water temperature but does cause a change in state, from liquid water to gas (vapor). Commonly used metric units for the energy fluxes in equation 2 are mega-Joules per square meter per day [i.e., MJ/(m2·d)].
- Equation 2 shows that the total energy at the surface of the unit area at any instance remains constant but is transformed into different forms of energy.
- Net radiation (Rn) is the main source of energy and portions of it are used to increase the temperature of the surface or surrounding air (H), cause plant growth via photosynthesis (M), evaporate water from the plants and soil (LE), and heat the ground (G).
From Equation 2, the LE can be calculated to estimate the amount of crop evapotranspiration (ETc):
Equation 3
LE = Rn + M – H – G
The LE in Equation 3 can be converted to equivalent crop evapotranspiration (ETc) as mass of water (e.g., kilograms of water).
- This is calculated by dividing LE by the latent heat of evaporation, which is the heat absorbed when a unit mass of water evaporates.
- For the range of air temperatures that occur in most growing seasons, the latent heat of evaporation for water can be assumed to be 2.45 mega-Joules per kilogram of water evaporated.
Review
Answer the following questions to help understand the concepts discussed in this lesson:

Earn an industry recognized micro-credential at: CSU Upskill.
Conservation of energy - total energy in an isolated system remains constant at a given point in time; the energy just exists in different forms (e.g., solar radiation, heat, etc.) or in different parts of the system.
Energy budget - also called energy balance; the sum of all forms of energy in a soil-plant-atmosphere system.
Latent Heat (LE) = the form of heat that causes water to evaporate from the plant and soil surface.
Net radiation = sum of solar radiation (or artificial light in the case of greenhouses) and thermal radiation (long-wave radiation emitted by objects).
Evapotranspiration (ET) - water lost from the soil-plant system through transpiration from plant leaves and evaporation from the soil surface.
